[ad_1]
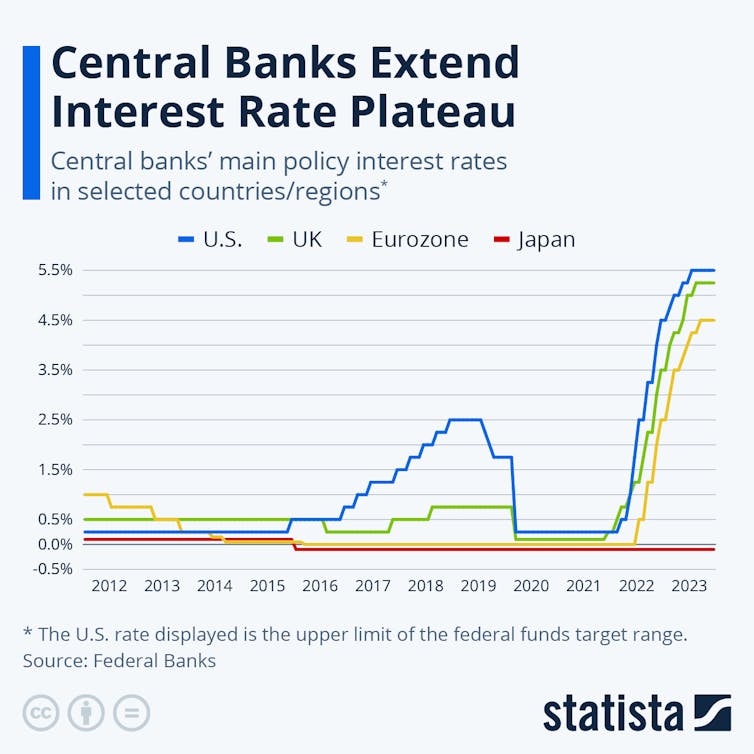
Central banks on either side of the Atlantic stored their most important rates of interest unchanged for the fourth successive month in December 2023. These charges are intently watched as a result of they set the minimal curiosity at which your financial institution borrows and lends. This determines the price of credit score for all corporations and households with mortgages or different loans.
The European Central Financial institution (ECB), the US Federal Reserve and the UK Financial institution of England have raised rates of interest sharply because the begin of 2022. This was in response to a surge in inflation – the annual enhance in client costs – far above the two% fee that each one these central banks now goal.
However UK inflation is taking longer to reply than that of the US or EU. This has renewed debate over whether or not fee cuts are the perfect or solely method to hold inflation beneath management. It has additionally induced a shift in opinions about which western economies are most susceptible to recession in 2024.
Learn extra:
Is the UK in a recession? How central banks resolve and why it is so exhausting to name it
Greater rates of interest are designed to subdue inflation by decreasing the quantity individuals spend. Companies and households are anticipated to avoid wasting extra when charges rise, in anticipation of better curiosity funds (though that doesn’t at all times occur). It’s additionally hoped they’ll borrow much less due to the additional curiosity they’d be charged. These with excellent loans are left with much less to spend on items and companies after paying their curiosity invoice.
Governments are additionally affected. Within the UK, curiosity on round 1 / 4 of presidency debt is now linked to inflation. This implies extra of the price range will get channelled into curiosity funds, leaving much less to spend on public companies, when the central financial institution raises charges.
This restraint doesn’t occur instantly, nonetheless. When debtors take out fixed-rate loans, they aren’t affected by larger base charges till the deal expires. Nearly one million UK debtors, for instance, are nonetheless on mounted charges of two% or under that may solely come up for renewal – at present, larger charges – within the first quarter of 2024. The ensuing delay of a yr or extra earlier than previous rate of interest rises kick in makes it exhausting for central bankers to know once they’ve raised charges sufficient to chill the financial system.
Learn extra:
UK bonds have hit a 25-year excessive – here is what meaning for the financial system
Elevating rates of interest also can restrain inflation by encouraging overseas traders to purchase bonds and different monetary belongings in a rustic’s forex. The ensuing influx of capital is more likely to strengthen its trade fee. This makes imports cheaper and will help to gradual the general rise in costs.
A stronger forex is particularly efficient for curbing inflation for economies that devour a excessive proportion of imports, such because the UK. However it additionally hurts exporters, and solely works if rates of interest rise above these of comparable economies. This can be one purpose why the Financial institution of England has raised its rates of interest quicker and additional than the ECB since February 2022.
Statista, CC BY
Divergence forward
Though they hiked charges in comparable style in 2022-23, these central banks are set to go other ways in 2024.
US charges are set to fall as inflation drops again in the direction of the two% goal, having already slowed to three.1% in November 2023 (from 6.4% in January). The US Federal Reserve has signalled two doubtless rate of interest reductions, totalling 0.75%, in 2024. That’s falling into line with traders’ expectations, which could be gauged by the costs they’re ready to pay for buying and selling or swapping debt due at a future date and by rates of interest on authorities bonds that mature a number of years from now.
Whereas the ECB’s ahead steering is much less clear, its governor has hinted at an identical downward path in 2024 as a result of projections now level to headline inflation dropping to 2.1% in 2025 – a yr sooner than beforehand predicted. Eurozone inflation has already slowed sharply, to 2.4% in November from 8.5% in February 2023, regardless of the ECB preserving its rates of interest decrease than the US and UK all through the latest tightening part. That’s largely as a result of, though member states set their very own fiscal coverage, EU guidelines hold them on a good rein in relation to spending and debt ranges.
In distinction the Financial institution of England has warned that its base fee, already larger than the EU’s, is more likely to keep at 5.25% “for an prolonged time period”. Inflation (on its focused client value index) slowed to 4.6% in October, effectively down from its peak above 11% in October 2022, however the common family is braced for extra price of residing will increase together with a mid-winter 5% rise within the power value cap. The latest weakening of the pound in opposition to the greenback has additionally added to industries’ uncooked materials prices, and will worsen if UK rates of interest fall too quickly.
Learn extra:
Inflation has affected the UK, US and Europe in another way – here is what this implies for rates of interest
Recession menace isn’t over
The UK financial system, whereas hardly rising this yr, has defied the Financial institution’s earlier forecast of a recession from the tip of 2022. However as a result of this inspired the financial institution into one other near-doubling of base charges – from 2.25% in October 2022 to five.25% from August 2023 – a UK recession in 2024 continues to be anticipated by some commentators. Sadly, client spending has been much less affected by larger borrowing prices than personal and public funding, which in the end drive financial development.
Extra ominously for US president Joe Biden, present rate of interest patterns recommend the US may be heading for recession in a presidential election yr. Most US GDP forecasts for 2024 stay within the 1.5-2.0% vary, however that’s effectively down from the 4.9% reached in third-quarter 2023. Towards this backdrop, the eurozone’s official forecast of 1.2% development in 2024 might be seen as a comparatively robust efficiency because it’s not anticipated to gradual as a lot because the US is predicted to in 2024.
So, debtors already hit by larger prices can count on some aid in 2024. However that’s partly resulting from rising concern that, with falling international commodity costs already serving to to subdue inflation, central bankers could have utilized the brakes too exhausting since 2022, endangering a worldwide restoration.
[ad_2]
Source link

