[ad_1]
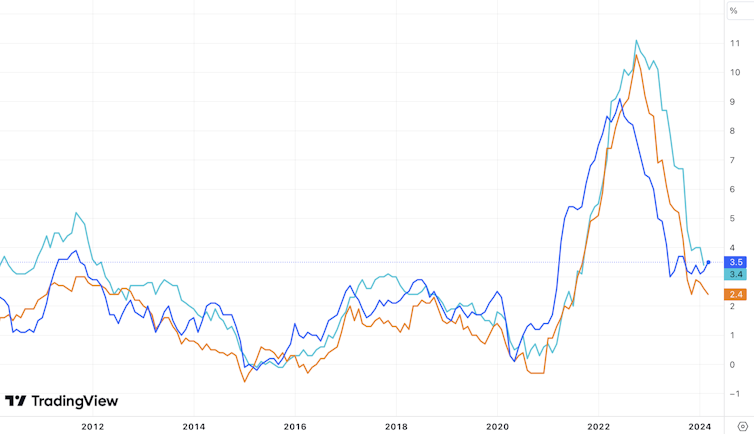
The 0.4% rise in US client costs in March didn’t appear to be headline information. It was the identical because the February improve, and the year-on-year rise of three.5% continues to be sharply down from 5% a 12 months in the past.
All the identical, this modest uptick in annual inflation from 3.2% in February has solid doubt on whether or not the US central financial institution, the Federal Reserve, can afford to chop headline rates of interest as quick because it has been signalling. To additional complicate issues, a niche has opened up between the US inflation price and that of different areas, notably the EU.
US inflation vs EU and UK
Buying and selling View
Monetary markets’ prompt response was bearish. They dumped shares whereas shopping for EU authorities bonds, in expectation of a lift from the European Central Financial institution slicing its charges sooner. Additionally they purchased the US greenback, anticipating it can strengthen when European charges come down. However how is that this prone to play out?
Can all of them be proper?
The US economic system has returned to regular growth after the COVID-19 pandemic disruption of 2020-22, whereas Europe is struggling to realize any development. This helps to clarify the distinction within the inflation figures.
The energy of the US economic system was already placing stress on the Fed to chop much less shortly. A better rate of interest helps to cease sturdy demand straining provide chains and making costs rise too quick. The quickening of consumer-price inflation provides the Fed an added incentive to be hawkish on charges – to persuade companies and households that it’s going to maintain financial circumstances tight till inflation falls again to the two% goal.
The rates of interest on advance purchases of US debt (the “Fed futures” market) present {that a} majority of merchants now anticipate the Fed is not going to drop its rate of interest from the present stage (of 5.25% to five.5%) to under 5% till December. Per week in the past, most thought this could have occurred by September.
The difficulty is that an prolonged interval of upper charges could possibly be very damaging as a result of there’s a lot debt within the system. Particularly, final 12 months’s wobbles within the US banking sector, and wider considerations about institutional traders uncovered to a stoop in industrial actual property, are sturdy incentives to scale back credit score prices earlier than too lengthy.
Consequently, few imagine the US headline rate of interest will nonetheless be at current ranges a 12 months from now. But the longer that inflation endures, the extra the stress to delay additional price cuts. Most People now imagine inflation will keep round 3% for the following 12 months, an expectation echoed in markets for property considered as defending in opposition to inflation (equivalent to gold and cryptocurrencies).
Election-year inflation risks
An particularly fraught presidential election race additionally limits the Fed’s manoeuvring room. The White Home has pitched its 2024-25 federal funds as serving to to subdue inflation, by decreasing working households’ dwelling prices and forcing corporations to pass-on value financial savings.
However whereas Joe Biden goals to spend US$7.3 trillion (£5.8 trillion) in pursuit of his plans, congressional opponents are prone to block most of the tax will increase supposed to pay for them.
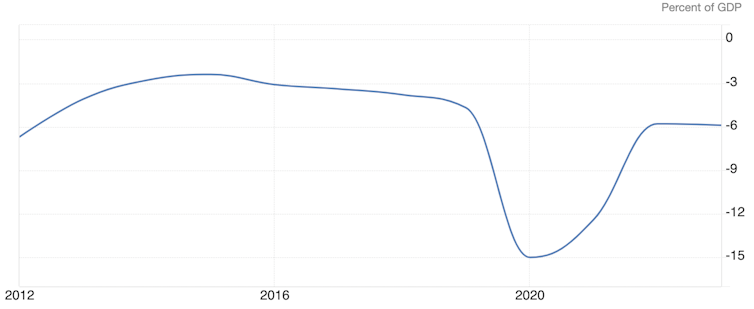
That’s prone to imply a continued widening of the US federal deficit, injecting extra demand and maintaining inflationary stress. That stress could possibly be worsened by the punitive tariffs that Republicans wish to impose on low cost imports, to which many Democrats are sympathetic. An more and more bipartisan push for tighter border controls would additionally increase US inflation danger, by stemming the influx of low cost labour that has stored unskilled wages down.
US federal deficit
Buying and selling Economics
The case for slicing anyway
Regardless of these caveats, monetary markets may nicely nonetheless be proved flawed concerning the velocity of US price cuts. Moreover the private-sector debt considerations, one extra potential justification for slicing sooner really pertains to inflation. Whereas central banks respect the standard knowledge that increased rates of interest scale back inflation, they can not disregard proof that the impact could also be reversed if charges are stored excessive for too lengthy.
When companies anticipate rates of interest to remain excessive, they increase costs to compensate, particularly if heavier debt repayments spur staff to ask for extra pay. Notably, the rising value of mortgages within the US was one of many elements in March’s inflation shock. The Fed can finest sort out this by sustaining the reassurance of decrease rates of interest, in order that lodging prices can fall.
In the meantime, China is grappling with falling costs, which may do even worse injury than an inflation overshoot. There may be nonetheless a chance of China making an attempt to flee this example by flooding the world with low cost items, and power prices falling sharply when the Russia-Ukraine struggle ends. This would depart central banks in Europe and America involved to cease their inflation falling too far, by slicing charges sooner than the market at present expects.

EPA
The Fed should lastly issue within the world draw back of holding agency whereas different central banks’ rates of interest fall. This is able to deal a double blow to the numerous nations, and non-US corporations, which have borrowed in US {dollars} to finance their growth plans. They’d pay comparatively extra on their greenback debt, whereas their native forex revenues would purchase fewer {dollars}, because the greenback strengthens as US rates of interest transfer comparatively increased.
The greenback’s world attain signifies that if the Fed doesn’t let headline charges fall, it may exacerbate a worldwide slowdown. That might rebound in opposition to American producers, particularly these now reliant on Europe, Latin America and Asia as main export markets. So when the ECB cuts charges, the Fed might be nonetheless anticipated to comply with, even when it means US inflation remaining above goal into 2025. This might imply one other increase to inventory costs, contemporary incentives to borrow more cash, and better instability for the years forward.
[ad_2]
Source link

