[ad_1]
Here’s what the report says, and what the overall scenario for leopards is like in India.

A marginal improve in total leopard inhabitants
Indian leopards (Panthera pardus fusca) are distributed throughout a wide range of forested habitats in India, Nepal, Bhutan, and elements of Pakistan. Being apex predators, they sit on the high of the meals chain, and thus play an important function in sustaining a balanced ecosystem. Like lions (Panthera leo), leopards got here to India from the west, most probably Ethiopia.
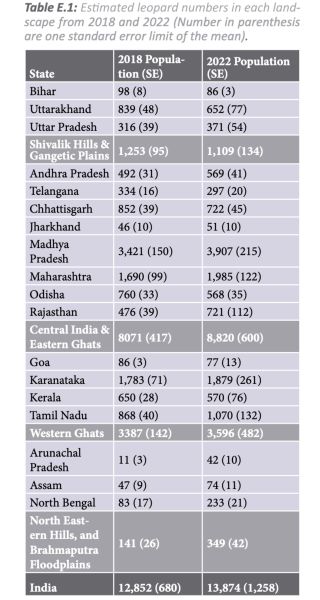
Based on the not too long ago launched report, Central India and Japanese Ghats has the best inhabitants of leopards (8,820), adopted by the Western Ghats (3,596), and the Shivalik Hills and Gangetic Plains (1,109). Statewise, Madhya Pradesh boasts of the most important inhabitants of leopards (3,907), adopted by Maharashtra (1,985), Karnataka (1,879) and Tamil Nadu (1,070).
“The info exhibits that the leopard inhabitants hasn’t grown the identical approach the tiger inhabitants has grown. It’s a marginal improve,” Wildlife Institute of India’s (WII) former dean Y V Jhala informed The Indian Specific. Nonetheless, he added that since leopards stay engaging targets for poachers, “it’s a matter of satisfaction to handle the established order”.

Lower in inhabitants in some areas
Nonetheless, leopard populations declined in a number of areas. The report confirmed that the Shivalik Hills and Gangetic Plains recorded a worrying 3.4% every year decline, happening from 1,253 in 2018 to 1,109 in 2022.
A number of states too reported a decline in leopard inhabitants. In Odisha the variety of leopards dropped from 760 in 2018 to 562 in 2022, and in Uttarakhand, the inhabitants declined from 839 in 2018 to 652 in 2022. Kerala, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, and Goa too reported inhabitants declines.
 Supply: Standing of Leopards in India, 2022.
Supply: Standing of Leopards in India, 2022.
One issue behind this may be the rise in tiger populations. Uttarakhand wildlife officers informed The Indian Specific that though leopard numbers stay steady in Rajaji and Corbett nationwide parks, the Ramnagar Forest Division has recorded a big decline in its leopard inhabitants probably resulting from elevated tiger density.
Different components embrace a lot of exterior threats, resembling poaching and habitat loss. Highway accidents are additionally a big explanation for leopard fatalities.
Advantages from tiger conservation efforts
Whereas an increase within the tiger inhabitants has been recognized to adversely affect the habitat and sources out there to leopards and different creatures decrease down the predator chain, tiger conservation efforts have additionally helped develop leopard populations.
Take, as an illustration, the Central India and Japanese Ghats panorama, which boasts of the most important leopards inhabitants. Wildlife officers informed The Indian Specific that “[the] leopard inhabitants on this panorama is rising, largely resulting from protecting measures underneath the umbrella of tiger conservation.”
The report said that “leopard densities are increased within the Tiger Reserves in comparison with exterior Protected Areas, even supposing tigers exert regulatory stress on leopards.”
Madhya Pradesh Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (Wildlife) Aseem Shrivastava spoke to The Indian Specific on the matter. He stated: “Tiger in Madhya Pradesh is an umbrella species. After we preserve the tiger, we additionally preserve the co-predators, the vegetation, and the entire habitat as a complete. The state has an excellent monitor document of tiger conservation and that safety has been prolonged to leopards.”
Shrivastava added that “the state has a very good administration of the prey base”, which has helped increase its leopard inhabitants.
Leopard-human battle stays a fear
Leopards’ adaptability when it comes to habitat and dietary preferences assist them to thrive in agro-pastoral areas, plantations, and close to human settlements. This, nevertheless, has led to rising leopard-human battle.
Based on the report, within the Shivalik area, roughly 65% of the leopard inhabitants is current exterior protected areas. The Uttarakhand Forest Division stated that 30% of all wildlife-caused human deaths and damage circumstances had been resulting from leopards (570 of almost 2,000 circumstances from the final 5 years).
A 2023 report states that Maharashtra has emerged because the worst-affected state, reporting 113 deadly assaults within the final seven years, whereas Karnataka reported over 100 human-leopard encounters. This escalation can largely be attributed to habitat loss, resulting from mining and different human actions.
In Kerala, from 2013 to 2019, there have been a complete 547 reported incidents of human-leopard battle, together with 173 livestock deaths or accidents (93 cattle, 2 buffalo, 78 goats), a Kerala state authorities report stated.
In Uttar Pradesh, assaults are attributed principally to the truth that protected areas are “lower than 10 km huge.” A 2019 analysis paper on UP’s Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary famous that “38% of the battle with leopards occurred when the sufferer was both inside or adjoining to a house. One other 40% of the battle was recorded in agricultural fields, and 11% of assaults had been on individuals who had been defecating in farmlands”.
In Tamil Nadu, the coffee-tea estates and different industrial plantations surrounded by forests are regularly occupied by leopards, since land is cheaper close to the sides of forests, plantation staff purchase these land for constructing homes, a 2017 analysis paper said.
[ad_2]
Source link

